Homoeopathy in Modern Healthcare: Myths & Facts
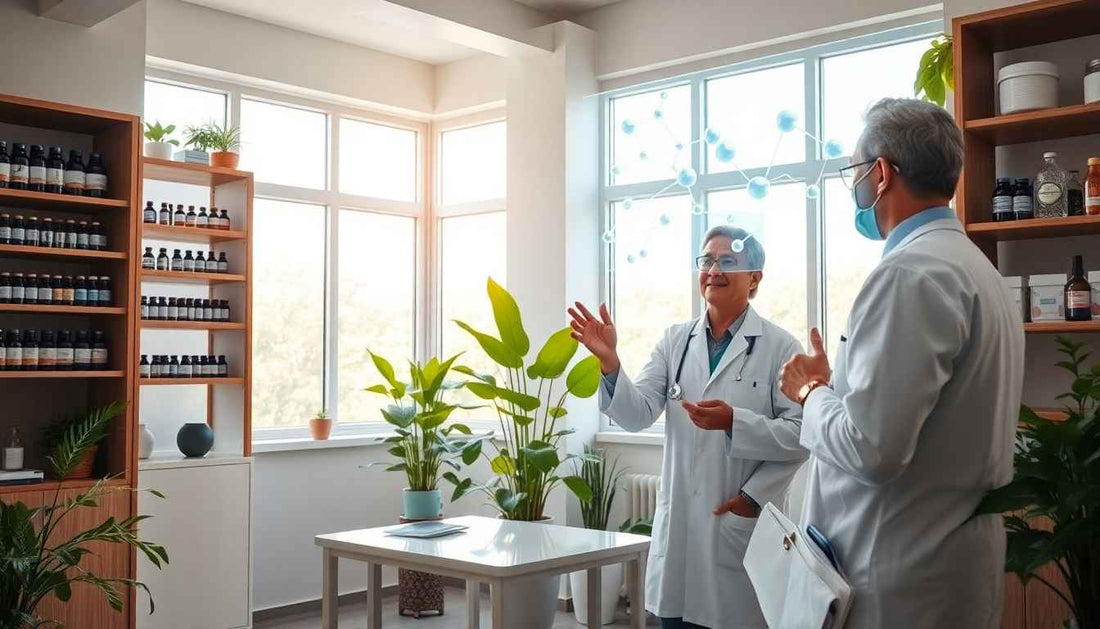
Homoeopathy in Modern Healthcare: Myths & Facts has become a significant topic of discussion among healthcare professionals and patients alike. While it has been practiced for over 200 years, misconceptions and skepticism often surround this alternative medicine system.
Homoeopathy, founded by Samuel Hahnemann in the late 18th century, operates on the principle of 'like cures like.' This means that a substance causing symptoms in a healthy person can be used to treat similar symptoms in a sick person. Despite its long-standing use, many individuals question its efficacy and principles.
One common myth is that homoeopathy is merely a placebo. Studies have shown that homoeopathic treatments can have effects beyond placebo. This is particularly notable in chronic diseases, where patients frequently experience significant improvements in their quality of life after homoeopathic treatment. Moreover, the NHS and various insurance providers have begun to recognize certain homoeopathic treatments, adding credibility to its practice.
Another prevalent misconception is that homoeopathy is ineffective for serious conditions. In reality, many practitioners use it as a complementary approach alongside conventional treatments, providing patients with a holistic treatment plan that considers both mental and physical health. Homoeopathy has been reported to alleviate various conditions, including allergies, asthma, migraines, and even depression, highlighting its potential role in modern healthcare.
Critics argue that research on homoeopathy is limited, but numerous studies have illustrated its benefits. For instance, a systematic review in 2015 concluded that homoeopathy can be more effective than placebos in certain cases. However, due to the subjective nature of medicine and personal experiences, this data should not be generalized across all patients.
In addition to addressing health issues, homoeopathy prioritizes patient-centered care. Practitioners often spend considerable time with patients, taking detailed histories and understanding lifestyle factors that contribute to health conditions. This comprehensive approach is increasingly important in the modern healthcare landscape that values individualized treatment.
Moreover, homoeopathy emphasizes safety. Unlike some conventional medications that may result in severe side effects, homoeopathic remedies are typically derived from natural substances and are diluted to the point where they are generally considered safe for all age groups. This aspect is particularly appealing to parents seeking alternatives for their children, as well as individuals wary of pharmaceutical side effects.
As we delve deeper into the integration of homoeopathy in modern healthcare, it is crucial to separate myths from facts. Medical professionals and patients should collaborate to create an evidence-based approach to treatment that respects both traditional and alternative practices. Ultimately, the effectiveness of homoeopathy should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, with patients encouraged to communicate openly with healthcare providers about their preferences and experiences.